
The common cause of a blocked Eustachian tube is from mucus and inflammation that occur with colds, throat infections, hay fever, etc. Also, if you have any condition that causes a blockage to the Eustachian tube, then the air cannot travel up or down. For example, some people may have a more narrow Eustachian tube than normal. However, the Eustachian tube in some people does not open as easily and so the pressure may not be equalised so quickly.
So, in most people, just normal swallowing and chewing allows air to flow up or down the Eustachian tube to quickly equalise the air pressure either side of the eardrum. The Eustachian tube is normally closed but opens from time to time when we swallow, yawn or chew. Why are some people affected more than others? Other situations where air pressure may quickly rise outside the ear is during scuba diving, diving to the bottom of a swimming pool, or rapidly descending in a lift (elevator). If the pressure inside the middle ear is not equalised quickly, then you can get ear pain. As a plane descends to land, the air pressure becomes higher nearer the ground. The most common example of barotrauma occurs to some air travellers. Air needs to travel up the Eustachian tube into the middle ear to equalise the pressure. To relieve the tensed eardrum, the pressure inside the middle ear has to rise quickly too. The tensed eardrum also cannot vibrate as well as it should and so you may also have dulled hearing.
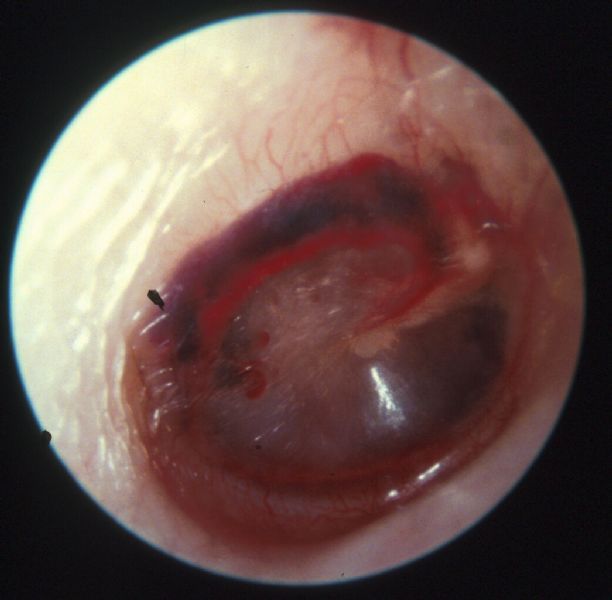
If the air pressure outside the ear quickly increases then this pushes the eardrum inwards which can be painful. The air on either side of the eardrum should be at the same pressure for the eardrum to vibrate and function normally.
This air space is connected to the back of the nose by a tiny channel called the Eustachian tube. The small space in the middle ear behind the eardrum should normally be filled with air. Barotrauma of the ear is the most common type of barotrauma. Barotrauma means damage to tissues caused by a difference in pressure between an air space inside the body. It is where you have ear pain and dulled hearing because of unequal pressure that develops between the air in the middle ear and the air outside the ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
